Bio Molecules
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids : DNA, RNA are important factors in heredity complete hydrolysis of DNA yields a pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and N - containing heterocyclic compounds.
DNA → β - D - 2 deoxyribose
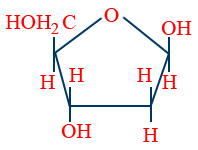
RNA → β - D - ribose

DNA → 4 bases : Adenine, thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
RNA → 4 bases : Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine.
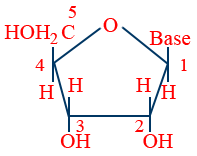
Nucleoside : A unit formed by attachment of base to 11 position of sugar is called nucleoside
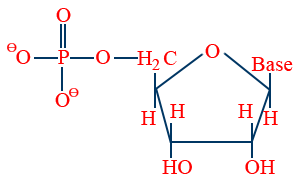
Nucleotide : A unit formed by attachment of phosphoric acid at 51 to nucleoside is called nucleotide
Di nucleotide : 2 nucleotides on adding give a dinucleotide
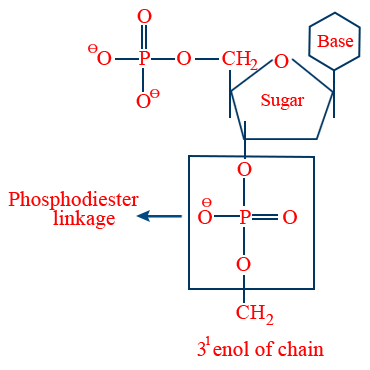
Nucleic acid :
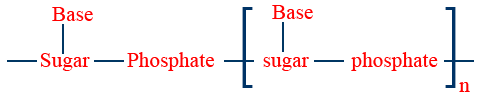
DNA is the basis of heredity and it gives the genetic information.
Part1: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 3:39
Part2: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 9:12
Part3: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 3:32
Part4: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 6:20
Part5: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 4:10
Part6: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 4:18
Part7: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 6:42
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.

