Animal Kingdom
Basis of Classification
- The kingdom animalia is characterised by heterotrophic eukaryotic organisms that are multi cellular and their cells lack cell walls. 'Animals word derived from the latin 'anima' which means 'air'/ breath/soul
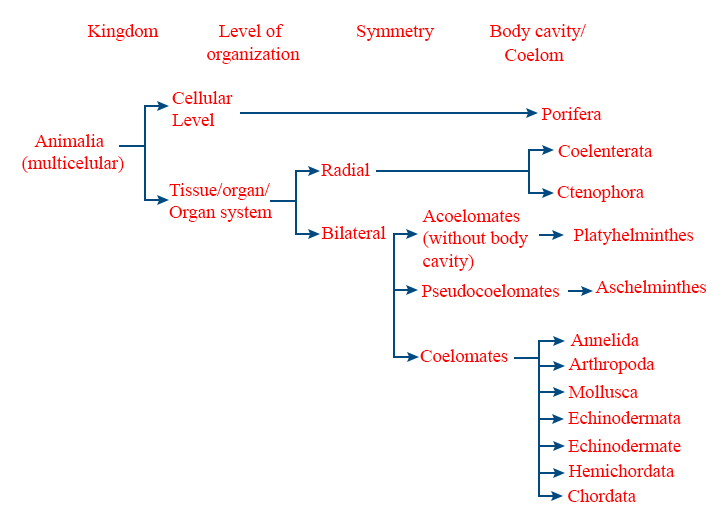
- Animal shows different grades of organization/Level of organisation.
(i) Cellular level: Division of labour (activities) Occur among the cells. Eg: spongers, mesozoans.
(ii) Tissue level : Cells performing the same function are arranged into tissues. Eg: coelenterates & ctenophores.
(iii) Organ level: Tissues grouped together to form organs each organ is specialised for particular function Eg: platyhelminthes.
(iv) Organ-system level: Organs join in system to perform basic functions. Eg: Aschelminthes to chordates - Symmetry - Body symmetry is the similarity of parts in different regions and directions of the body. klhen the body is divisible into equal halves by any plane it is called asymmetrical (Eg: Amoeba, sponges)
- Radial symmetry: (Radiata-animal), Body can be divided into equal parts by any plane passing through the centre from top to bottom. Eg: cnidarians, ctenophores, adult chinoderm.
- Bilateral symmetry (Bilateria-animal) Body can be divided into equal right and left halves in only one plane. Eg: platyhelminthes, nemathelminthes, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, chordata.
- Germ layers: Diploblastic animals have the body cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, (outer ectoderm; inner-ectoderm, in between mesoglea is present) Eg: coelenterates, ctenophores
- Triploblastic animals have three germinal layer. Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm. Eg: Platyhelminthes to chordates.
- Coelom is a fluid filled body carify lying between the outer body wall and inner gut wall. animal possessing coelom are called coelomates.
Eg. annelids, mollusca, arthropoda, echinoderms, hemichordates & chordata. - Pseudocoelomate: In some animals, body cavity is present but not completely lined by mesoderm, instead. mesoderm is present as scattered pouches in between the ectoderm and endoderm.
Eg: Aschelminthes. - Coelom is absent are called acoelomates.
Eg: sponges, coelenterates, ctenophores, Platyhelminthes. - Segmentation is the division of body into parts / segments two types: Metameric segmentation & pseudometamerism.
Eg: earthworm, shows metameric segmentation and this is known as metamerism.
Eg: Tapeworm, segmentation if found only outside - Digestive system : In complete digestive system has only a single opening to the outside body that serves as both mouth and anus.
Eg: Coelenterates, ctenophores, platyhelminthes. - Complete digestive system has two openings; mouth and anus. eg: Aschelminthes to chordates.
- Circulatory system: (i) Open (ii) Closed.
Open circulatory system → body cells, tissues are directly bathed in the blood pumped out of heart, as blood flows in open space. eg: Arthropods, hemichordata etc (iii) closed circulatory system : Blood flows through a series of blood vessels with different diametre. eg : Annelids, Mollusca, Chordates. - Notochord is mesodermally derived rod like structure formed during embryonic development. Animals with notocord are called chordates.
- Classification of animals
Part-1: View this video for the topic from 0:51 to 9:36
Part-2: View this video for the topic from 0:13 to 8:30
Part-3: View this video for the topic from 0:09 to 16:17
Part-4: View this video for the topic from 0:14 to 11:47
Part-5: View this video for the topic from 0:10 to 11:00
Part-6: View this video for the topic from 0:10 to 16:04
Part-7: View this video for the topic from 0:11 to 3:33
Part-8: View this video for the topic from 0:09 to 4:41
Part-9: View this video for the topic from 0:09 to 9:14
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.

