Solid State
Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
- Crystal lattice(s): The regular three dimensional arrangement of constituent particles (also called as points) is called crystal lattice.
- It expands infinitely along all the coordinate axis
- A portion of crystal lattice can be shown as follows
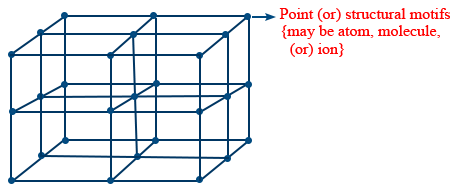
- Unit cell(s): Smallest repeating structural unit in crystal lattice is known as unit cell.
- It can be shown as follows
- There are mainly two types of unit cells (i) Primitive unit cell (ii) Centered unit cell
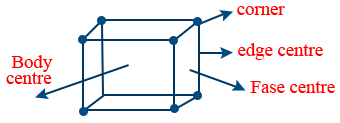
- Primitive Unit Cell: If points occupy only at corner of unit cell is called primitive unit cell.
- Centered Unit Cell: If points occupy in addition to corner either face centre (or) body centre or edge centre are called Centered Unit Cell.
- Centered unit cells again of mainly three types.
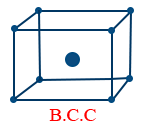
(i) Body centered cubic crystal
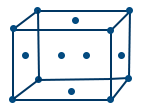
(ii) Face centered cubic crystal (or) cubic close pack
(iii) End centered cubic crystal. - Body centered cubic crystal (B.C.C): If points occupy in addition to corner at body centre of unit cell is called B.C.C lattice.
- Face centered cubic lattice (F.C.C): If points occupy centre of all faces in addition to corner are called F.C.C.
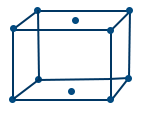
- End centered cubic lattice (E.C.C): If points occupy only at a pair of opposite face centres in addition to corner called end centre unit cell.
View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 8:55
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.
Density of unit cell = \tt \frac{mass \ of \ unit \ cell}{volume \ of \ unit \ cell}
d = \frac{Z.m}{a^{3}} = \frac{ZM}{a^{3} \times N_{A}} kg/cm^{3}
[Mass of an atom m = \frac{M}{N_{A}}]
(The density of the unit cell is same as the density of the substance.)
where,
d = density of unit cell, M = molecular weight
Z = number of atoms per unit cell, NA = Avogadro number
a = edge length of unit cell.

