Biodiversity and its Conservation
Biodiversity-Concept, patterns, importance
- Biodiversity can be defined as the vast array of species of microorganisms, algae, fungi, plants and animals occuring on the earth either in the terrestial or aquatic habitat.
- Although India has only 2.4 percent of the world land area, its share of global species diversity in 8.1%. It is one of the 12 mega - biodiversity countries of the world which has about 45,000 species of plants and twice as many species if animals.
- species diversity decreases as we move away from the equator towards the poles. It increases in temperate areas but reaches the maximum is tropical rain forest. Maximum diversity occurs in Amazon rain forest of south America with 40,000 plant species, 3000 fish species, 1300 birds, 427 mammals, 427 amphibians, 378 reptiles and more than 1,25,000 invertebrates.
- Some reasons behind the maximum the maximum biological diversity of tropical regions
⇒ Prolong evolutionary time : speciation is generally the function of time
⇒ Constant environment
⇒ high productivity : due to more solar energy - German naturalist and geographer Alexander Von Humboldt, while exploring the wildness of south American jungles found that within a region, the species richness increased with increasing area but upto certain limit.
- The relationship between species richness and area turned out to be a rectangular hyperbola for awide variety of toxa on, alogarithmic scale it is a straight line
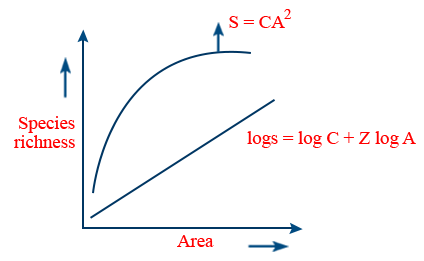
- S → species richness
Z → regression co - efficient
C → Y intercept ; A → Area - Regression coefficient Z = 0.1 − 0.2 regardless of taxonomic group
Z = 0.6 − 1.2 for frugivorous birds and mammals of tropical forest of different continents, with the slope 1.5 - Rich diversity is essential not only for ecosystems but also for human race survival.
- Biodiversity is essential for stability of an ecosystem. Communities with more species tend to be more stable than those with less species which is able to resist occasional disturbance.
- Several thousand species of edible plants and animals are known. However, 85% of the world's food production is met by cultivating less than 20 plant species.
- Wheat, corn and Rice alone yield nearly 2/3 rd of food production
- Biodiversity is also used as a source material for breeding improved verities. In this way disease resistant and high yielding varieties of crops and fruits have been developed. Also hybrid animal varieties have been produced to increase the milk production, meat and eggs etc
- A variety of plant species such as cotton, flax, hemp, jute, Agaus, Abaca are the major sources of fibres.
- Useful products
⇒ Gums, resins, dyes, latex, tannins, paper, tea, coffee.
⇒ from animal species ⇒ silk, waxes, honey, lac, Ivory, horns, antless.
⇒ Therapeutic properties like quinine from cinchona ledgeriana
⇒ Taxol from Taxus brevifolia, Taxus baccata [yew tress] to treat cancer. - Animals are used for biological and medical research. New medicines are tested first on animals. Animals preceded humans in space.
- Biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services such as replenishing O2 through photosynthesis, Pollination though bees, regulation of global climate, microbial waste treatment etc.
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.

