Animal Kingdom
Chordates up to class level
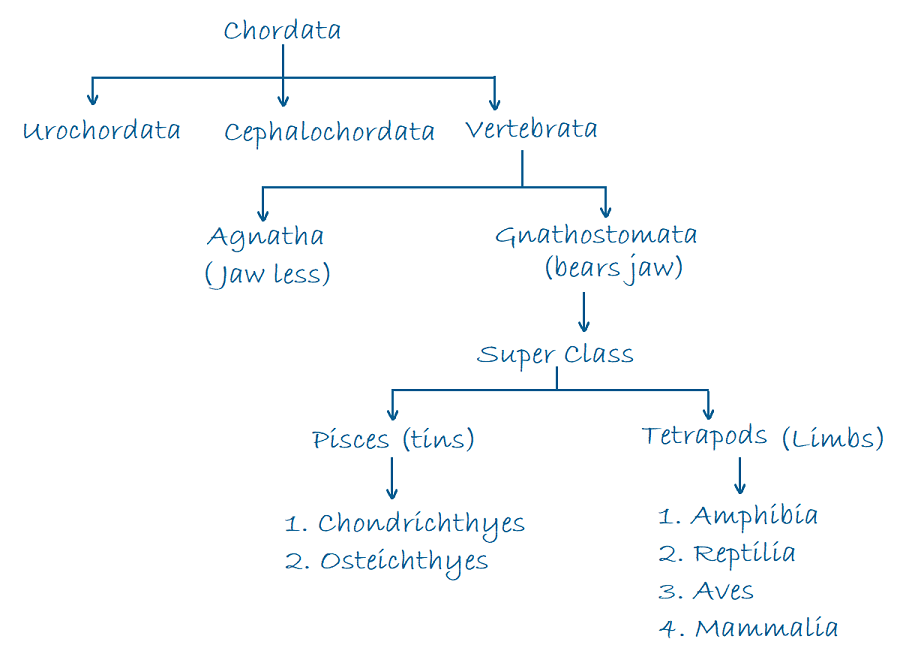
Phylum : Chordata
- Phylum chordata are characterised by the presence of a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord and paired pharyngeal gill slits.
- These are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic coelomate with organ system level organization. They posses post anal tail and a closed circulatory system.
- Phylum chordata is divided into 3 subphylum; urochordata, cephalochordata and vertebrata.
- Urochordata and cephalochordata are referred as protochordata and they are exclusively marine animals.
- In urochordata (tunicate) notochord is present only in the larval tail and disappears in adult.
- Larva (ascidian tadpole) undergoes retrogressive metamorphosis (change from better developed larva to less developed adult)
- Examples:
i) Herdmania (Sea squirt)
ii) Ascidia
iii) Salpa
iv) Doliolum - In cephalochordata, notochord extends upto anterior end of the body and present through out the life. Pharyngeal gill slits are numerous in number and are better developed.
- Example: branchiostoma (amphioxus lancelet)
- Vertebrata are advanced chordates that have cranium around brain. It posses notochord during embryonic period. Laver it is replaced by vertebral column (back bone in adults)
- They have ventral muscular heart with 2/3/4 chambers, kidneys for excretion and osmosegulation and paired appendages which may be tins / limbs.
- Jawless vertebrates (agnatha) are most primitive of all craniates. Mouth doesn't posses jaws. They don't have paired appendages. They are cold blooded which existing in class named cyclostomata.
- Class cyclostomata (circular mouth) have 6-15 pairs of gilt slits for respiration. Body is eel like tail is compressed, skin is smooth without scales and tins.
- They are marine but migrate for spawning to freshwater. Their larvae after metamorphosis return to ocean cranium and vertebral column are cartilaginous.
- The heart is two chambered. Circulation is closed type kidney is mesonephric. 8-10 pairs of cranial nerves are present. Fertilization is external. Larva is ammocoetes.
- Examples:
Petromyzon (Lamprey)
Myxine (Hagfish)
Class Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous fish) - Mostly marine bears cartilaginous endoskeleton exoskeleton consists of placoid scales which are dermal in origin.
- They have 5-7 pairs of lamelliform gills. Gills are not covered by opercula except chimaera. Heart is 2 chambered, kidneys are mesonephric, uricotelic.
- Mouth is centrally placed. 4 spiral valve named scroll valve is present in intestine. Digestive tract leads to cloaca.
- Only inner ear is present, have 3 semicircular ducts, lateral line sense organs are well developed. Kidneys are mesonephric (urea is nitrogenous waste).
- Sexes are distinguishable externally. Fertilization is internal and many of them are viviparous. Some have electric organs (eg: Trygon). They are cold blooded (poikilothermous)
- Examples:
1. Scoliodon (dog fish)
2. Pristis (saw fish)
3. Carcharodon (great white shark)
4. Trygon (sting ray)
5. Torpedo (electric ray)
Class osteichthyes (Bony fishes) - Osteichthyes includes all members of lung fishes and are both fresh and marine water fishes. Body has three regions, head, trunk and tail. Tail is homocercal.
- Scales of 3 types: ganoid, cycloid, ctenoid. Placoid scales are absent. Mouth is horminal, digestive tract leads to anus. Cloaca is absent in bony fishes.
- Swim/air bladder is present which facilitates floating and may function as respiratory organ gills are 4 pairs and covered by opernaculum.
- Heart is 2 chambered sinus venosus and conus arteriosus is present kidney is mesonephric. (ammonotelic/ureotelic)
- 10 pairs of cranial nerves are present. Well developed lateral line system is present.
- Sexes are separate, fertilization is external mostly oviparous and development is direct.
Examples:
Marine - exocoetus (flying fish) can glide in air
Hippocampus (sea horse) the male has breed pouch.
Freshwater : Labeo (Rohu), Catla (Katla)
Aquarium : Betta (fighting fish)
Pterophyllum (Angel fish)
Gambusia is predatory of mosquito larvae.
Class Amphibia (two life) - They are cold blooded, amphibious in nature present without scales, oviparous, vertebrates, Head distinct, trunk elongated. Neck and tail may present / absent.
- Skull is dicondylic, brain is poorly developed. Cranial nerves (co pairs) are present. Limbs usually 2 pairs (tetra pod) some limbless.
- Pigment cells (chromatophores) are present, exoskeleton is absent, endoskeleton mostly bony. Notochord doesn't persist.
- Heart is three chambed (2 auricles + 1 ventricle) sinus venosus is present. Kidneys are mesonephric (uricotelic)
- Ear consist of middle and inner ear. Tympanum covers middle ear which has single ossicle called columella auris.
- Sexes are separate. Fertilization - external, females are oviparous. Development is indirect. Amphibians are only fresh water animals, not found in sea.
- Examples:
1. Bufo (Toad)
2. Rata (frog)
3. Hyen (Tree frog)
4. Salamander (salamander)
5. Ichthyophis (Limbless amphibian)
Class reptilia
- First Class of vertebrates which has dry horny scales or scutes covered skin. This class name refers to the mode of cocomotion. Study of reptiles are called as herpetology.
- They are terrestrial, creeping / burrowing oriparous, cold blooded, tetrapodal vertebrates. Limbs are two pairs, and pentadactyl. (limbs are absent in few lizards and all snakes)
- Mouth is terminal bearing conical teeth - pleurodont in lizard and snake, thecodont in crocodiles. Teeth are absent / replaced in turtles.
- Endoskeleton is bony. Skull is monocondylic alimentary canal terminates into cloacal apertune. Two systemic arches are present.
- Heart is 3 chambered (usually), except cnecodile (4 chambered). Respiration by lungs throughout life. Kidneys are metanephric (uricotelic). Cranial nerves are 12 pairs.
- Jacobson's organ (vomeronasal organ) is present on roof of mouth act as olfactory (smell) organ. It is well developed in snake and lizard.
- Sexes are separate, male has copulatory organ fertilization is internal mostly oviparous, embryonic membrane appears during development. No metamorphosis, parental care is absent.
- Examples:
Calotes (Garden lizard)
Hemidactylus (wall lizard)
Chelone (Turtle)
Testudo (Tortoise)
Naja (Cobra)
Bungarus (Krait)
Class Aves
- Birds are feathered bipeds, air breathing, freely flying warm blooded vertebrates often they are described as "glorified reptiles".
- Body is boat shaped and streamlined. It is divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail. Bean is present which lacks teeth.
- Limbs are two pairs, forelimbs are modified as wings for flying. Hind limbs / legs are large and adapted for walking, wading, hopping and swimming.
- Legs bear horny epidermal scales. Skin is dry without any glands. Only cutaneous gland is uropygial or preen gland at the base of the tail. Sweat glands are absent. Oil/preen glands are absent in ostrich and parrot.
- Endoskeleton is bony but delicate and light. Bones are pneumatic / hollow and have no marrow. The largest and most powerful muscle is pectoralis major.
- Skull is monocondylic. The last 3/4 fused tail vertebrate form a structure called pygostyle. Synsacrum is formed by fusion of posterior thoracic, lumbar, sacral and anterior caudal vertebrae.
- The forked bone furcula formed by fusion of two chlorides and inner clavicle is called wishbone.
- Alimentary canal contains crop for storing and softening food. Gizzard is for cuisine, food. Respiration takes place in lungs, which contains of major air act.
- Voice box lies at the junction of trachea and bronchi is called as syntax. Larynx is without vocal cord.
- Heart is completely 4 chambered. Sinus venosus is absent. Only right aortic arch is present in adults renal portal system is vestigial.
- Kidneys are metanephric excretion is uricotelic. Urinary bladder is absent. Cranial nerves are 12 pairs middle ear contains single ossicle.
- Eyes posses nictitating membrane. Pecten present in this helps in the nutrition of eye ball. It is found in all birds except kiwi.
- Sexes are separate. All are oripavous with only single functional ovar and oviduct (mullerian duct). Development is direct birds are homeotherms.
- Examples:
Corvus (crew)
Psittacula (Parrot)
Paro (Peacock)
Neophron (rupture)
Class Mammalia
- They are terrestrial warm blooded animals. Some have gone back to water eg: whales. Occur is all sorts of habitats. Skin is glandular and covered with epidermal hair.
Glands
Sudorfic glands → Sweat
Sebaceous glands → Oil - There are two pairs of pentadactyl limbs which helps for doing various activites endoskeleton is bony, mouth is small. Buccal cavity has true salivary glands. Teeth occur in both jaws.
- External ear/pinna with an external auditory meatus inner and middle ear present. Respiration occurs by lungs. Heart is 4 chambered (2 auricles, 2 ventricles)
- Fertilization is internal sexes are often distinguishable except egg layering monotreme, mammals are viviparous. Development is direct. Body temperature is regulated (Homeothermy)
- Examples: Oviparous - Ornithorhynchus (platypus) Viviparous Macaca (Monkey), Equus (Horse), Elephants, Felis (Cat), Panthera leo (Lion), Pteropus (flying fox) etc.
Part-1: View this video for the topic from 0:26 to 12:43
Part-2: View this video for the topic from 0:22 to 6:05
Part-3: View this video for the topic from 0:15 to 6:46
Part-4: View this video for the topic from 0:13 to 5:52
Part-5: View this video for the topic from 0:15 to 6:10
Part-6: View this video for the topic from 0:13 to 7:00
Part-7: View this video for the topic from 0:09 to 10:07
Part-8: View this video for the topic from 0:16 to 8:54
Part-9: View this video for the topic from 0:12 to 7:08
Part-10: View this video for the topic from 0:13 to 7:55
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.