Surface Chemistry
Catalysis, Activity and Selectivity
- (a) Catalyst (Berzelius): It is a substance that can alter the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
(b) Positive catalyst: A catalyst that increases the rate of a reaction, is called positive catalyst. Fe in Haber process is a positive catalyst.
(c) Negative catalyst (or) reaction poison: A catalyst that decreases the rate of a reaction, is called negative catalyst. Acetanilide (or glycerol or H3PO4) acts as negative catalyst for the decomposition of H2O2
(d) Catalysis: The phenomenon of action of catalyst is called catalysis.
(i) Auto catalysis: A product of a reaction works as catalyst. The rate of reaction increases with time. 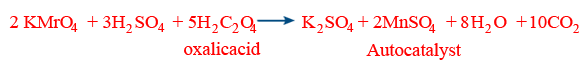
- (ii) Induced catalysis: Occurrence of a reaction catalyses some other reaction.
Na3AsO3 + O2 air → No reaction.
Na2SO3 + Na3AsO3 + O2 → Na2SO4 + Na3AsO4
(iii) Homogeneous catalysis: Catalyst and the reactants are in the same phase.
(a) Acidic hydrolysis of sucrose: 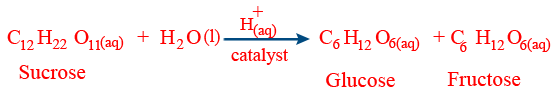
- (b) Lead chamber process: 2SO_{2(g)}+O_{2(g)}\xrightarrow[]{{NO(g)}}2SO_{3(g)}
This reaction was explained by Clement & Desormes as follows
NO+\frac{1}{2}O_{2(g)}\rightarrow NO_{2};
NO2 + SO2 → NO + SO3
(iv) Heterogeneous catalysis: It is type of catalysis in which the catalyst and reactants are in different phases.
Eg: (i) Contact process: 
(ii) Hardening of vegetable oil
Vegetable\ oil_{(l)} + H_{2(g)}\xrightarrow[]{{Ni_{(s)}}}Vegetable \ ghee
(iii) Haber process
- (v) Mechanism of Heterogeneous catalysis: In the adsorption releases energy, that decreases the activation energy of reaction. More vulnerable part and proper orientation of molecules for attack are available. Adsorbed molecules get activated/atomised and react to give products. Finally, products get adsorbed and make the surface available for adsorption of other molecules of reactants.
(vi) Activity of a catalyst depends upon extent of chemisorption. The ability of a catalyst to direct a reaction to produce particular product is called selectivity. 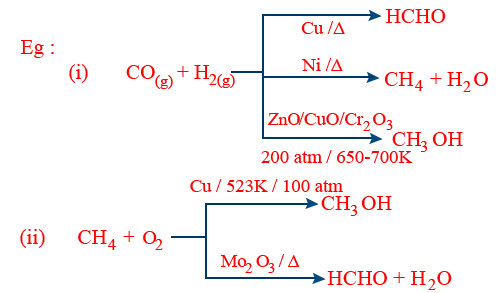
(vii) Heterogeneous catalysis some times, require a promoter to increase the activity of the catalyst. Eg. Mo acts as promoter for Fe in Haber process
* Promoter increases the surface area of catalyst to increase its activity.
(viii) Certain substances are preferentially adsorbed on active sites of catalyst to decrease the activity of a catalyst. Eg: As, Co etc., These are called catalytic poisons or anti catalysts.
(ix) Shape selective catalysis: When the activity of catalyst depends upon the pore (cavity) size and size of reactants and products, the catalysis is called shape selective catalysis. The pore size ranges between 260 to 740 pm
eg: ZSM-5 is a zeolite (silicate) that acts as shape selective catalyst to convert CH3OH to gasoline
\tt CH_{3}OH\xrightarrow[-H_{2}O]{{ZSM-5}}CH_{2}\xrightarrow[]{{Polymerises}}gasoline
(x) General formula of zeolites is Mx/n (AlO2)x (SiO2)y . m H2O. n is valence of metal M.
Eg: Permutit Na2Al2Si2O8.H2O
(xi) Characteristics of catalysis:
(a) A catalyst may undergo physical changes only
(b) Only a small quantity is required.
(c) A catalyst activates the rate of a reaction but cannot start it.
(d) Activity of a catalyst is maximum at a certain temperature.
(e) It decreases the activation energy for forward reaction, backward reaction and also threshold energy, equally.
(f) It gives a new mechanism to the reaction.
(g) It does not change the energy of the reaction.
(h) It does not change the extent of the reaction.- (*) Trick to understand characteristics e, f and g can be understood more clearly with following graph.
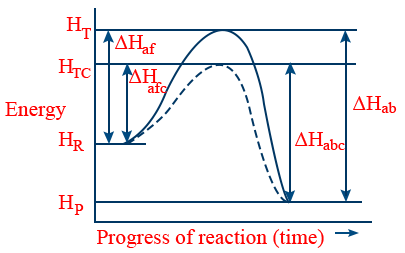
- Unbroken graph: Without catalyst
Broken graph : with catalyst
HT: Threshold energy without catalyst.
HTC : Threshold energy with catalyst.
HP : Energy of products.
HR : Energy of reactants.
Haf and Hafc : Activation energy for forward reaction without and with catalyst.
Hab and Habc : Activation energy for backward or reverse reaction without and with catalyst.
ΔH : Energy of reaction = HP − HR = Haf − Hab
Note: This graph for exothermic reaction. - Enzyme catalysis:
(i) Enzymes are natural proteinous bio catalysts that exist in colloidal state. 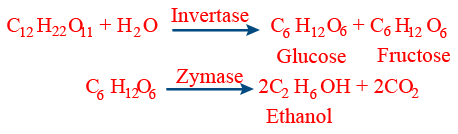
- Characteristics of enzymes:
(1) Enzymes are specific in nature. It is also called lock & key system.
(2) Enzymes are highly efficient. These increase the rate of reaction minimum to 106 times.
(3) In human body most of the enzymes are active at 7.4 pH approximately but outside the human body their optimum activity is of 5 to 7 pH.
(4) Sometimes a non-protein part called co-enzyme, is present with enzyme to increase its efficiency. Such a part is called apoenzyme and the combination as holoenzyme.
(5) Generally heavy metal ions poison the activity of enzymes.
(6) Enzyme having two binding sites are called allosteric enzymes. - Mechanism of enzyme catalysis (lock and key system):
Step-I: A fast reaction of binding of substrate 'S' an active site of enzyme 'E'. E + S → ES (complex)
Step-II: A slow reaction of formation of products from the complex ES is rate determining step.
ES → P(Products) + E
Part1: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 8:00
Part2: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 7:58
Part3: View the Topic in this Video from 0:08 to 15:53
Disclaimer: Compete.etutor.co may from time to time provide links to third party Internet sites under their respective fair use policy and it may from time to time provide materials from such third parties on this website. These third party sites and any third party materials are provided for viewers convenience and for non-commercial educational purpose only. Compete does not operate or control in any respect any information, products or services available on these third party sites. Compete.etutor.co makes no representations whatsoever concerning the content of these sites and the fact that compete.etutor.co has provided a link to such sites is NOT an endorsement, authorization, sponsorship, or affiliation by compete.etutor.co with respect to such sites, its services, the products displayed, its owners, or its providers.

